While on work experience, Ross Mcgowan of Bishop Stortford College looked into the role the cloud is playing in the digital revolution.
What is “The Cloud?”
The cloud is formally known as cloud computing. It refers to storing and accessing data and programs over the Internet instead of locally stored on a computer's hard drive. Therefore “the cloud” is simply a metaphor for the Internet.
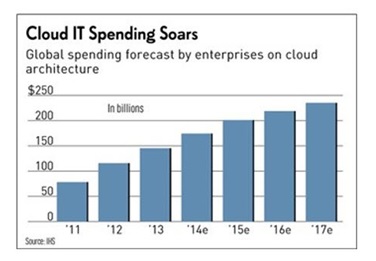
The majority of people use a cloud computing system on a daily basis e.g. any email which can be accessed from the internet can be considered cloud computing. By 2017, it is forecast that enterprise spending on the cloud will reach $235.1 billion.
There are four types of cloud deployment models:
- Public cloud – In a public cloud information uploaded by a user can be shared or extracted by anyone one else without the user knowing. So the user has no control of the information uploaded.
- Private cloud – In a private cloud the information can be controlled by the user, and the information can not be shared between different organisations. When compared, private clouds are more expensive but a lot more secure.
- Hybrid cloud – This is the combination of using a private and public cloud. This is also known as cloud bursting and is particularly useful for fluctuations in storage requirements.
- Community cloud – This cloud is used for sharing information between specific organisations “within a community.”
What are the benefits?
- Accessibility – Systems and data become more mobile and can be synched across various sessions, various devices and various locations. This gives workers the flexibility to work from anywhere.
- Cost - storing data locally is generally higher than storage in the cloud and often cloud services use SaaS (software as a Service) payment models which means payments are smoothed out over a period of time.
- Automatic updates – software updates and maintenance are conducted remotely and automatically by cloud computing suppliers, freeing up the customer’s time and resources for other tasks.
Are there concerns with adopting cloud computing?
- Security – By storing data in the cloud a company’s sensitive information is potentially being trusted to a third-party cloud service provider. Data stored online may be prone to attacks from hackers.
- Reliability – There is a threat to continuation of service. Vital information could become inaccessible and work can be brought to a halt for whole businesses should an internet connection lost or the cloud service provider have an outage.
Integration with other aspects of the digital revolution
Cloud computing is playing an essential part to the development of digital technologies that push the boundaries of innovation, and should help to make our lives easier, cheaper and more practical. With ever increasing numbers of devices becoming connected (see 'Internet of Things' - From cars to cookers, it's a connected revolution) and therefore increasing amounts of data being generated, the cloud facilitates its storage with almost limitless capacity.
Sources and further reading:
http://uk.pcmag.com/feature/16824/what-is-cloud-computing
http://computer.howstuffworks.com/cloud-computing/cloud-computing.htm
http://www.enterpriseirregulars.com/73127/roundup-cloud-computing-forecasts-market-estimates-2014/